理工学院光电工程系卢惠辉副教授课题组在期刊Light: Science & Applications发表重要研究成果
最近,暨南大学理工学院陈哲教授团队的卢惠辉副教授(通信作者)课题组联合法国国家科研中心(CNRS)Thierry Grosjean研究员(通信作者)团队、瑞士洛桑联邦理工学院(EPFL)Hans-Peter Herzig教授团队,在Nature出版社著名期刊Light: Science & Applications (IF = 14.098) 发表重要合作研究成果:Magnetic spin–orbit interaction of light (光的磁自旋-轨道转化)。该研究通过微纳尺寸的介质多层膜产生的布洛赫表面波(Bloch Surface Wave)被光的磁场左旋/右旋调控的原创性方案,率先理论和实验验证了光的磁自旋-轨道转换的物理机制应用于光场调控。
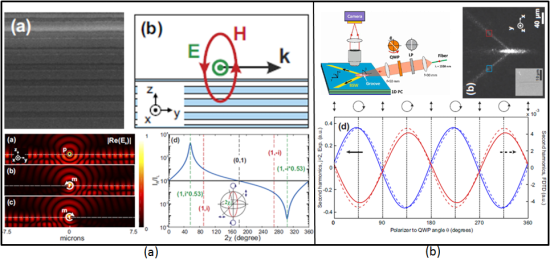
亚波长的介质多层膜结构产生布洛赫表面波可以为TE或TM形式,这为光的磁自旋-轨道转化调控奠定了很好的技术手段和平台基础。审稿人认为文章报道了一个非常具有吸引力的光学现象,因为产生定向光波的自旋-轨道转化是由光的磁场驱动的,这个首次发现和之前由光的电场驱动不一样。(The manuscript reports a very interestingphenomenon in optics: the direction excitation of guided wave arising from spin-orbit interaction but driven by the magnetic field of light, instead of by the electric field of light as in all previous experiments so far. This is certainly a very interesting finding, it evidences that the spinning nature of the magnetic field can play a role in spin-orbit interaction and as a manifestation of the quantum spin Hall effect of light.)
卢惠辉课题组与法国国家科研中心(CNRS)已合作发表高水平论文6篇,双方将在弱电场电光调制与探测、手性纳米天线和表面光波的光场调控等高水平研究继续深化合作。
Light: Science & Applications (Nature Publishing Group) volume 7, 24 (2018)
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-018-0018-9
